Introduction to the United Arab Emirates
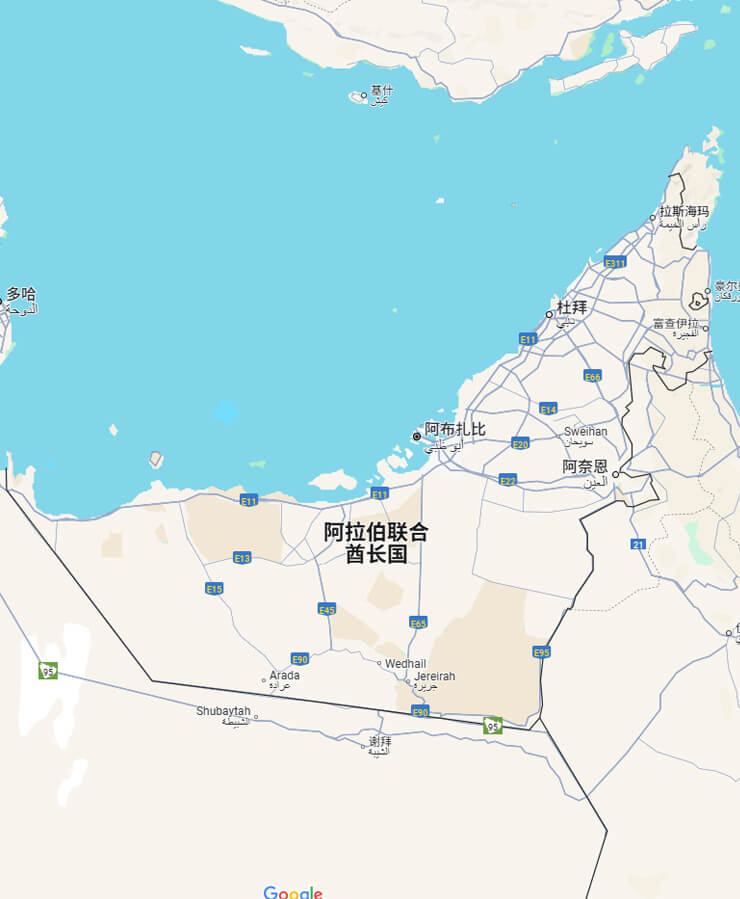
The eastern portion of the Arabian Peninsula is home to the United Arab Emirates, or "UAE," which shares borders with Qatar to the northwest and the Persian Gulf to the north. Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ras Al Khaimah, Ajman, Fujairah, and Umm Al Quwain are the seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates. Natural gas and oil resources are abundant in the United Arab Emirates. This West Asian desert nation is referred to as the "flower in the desert" and is well-known for producing oil.
Situated in the eastern region of the Arabian Peninsula, the United Arab Emirates shares borders with Qatar to the northwest, Saudi Arabia to the south and southwest, Oman to the east and northeast, and the Persian Gulf to the north. Plains, mountains, and depressions make up the majority of its terrain, which has a tropical desert climate. The natural gas and oil resources are abundant. Low-lying lowlands make up the coastal regions. The peninsula's northern region is mountainous. 2,438 meters above sea level is the tallest mountain in the Hajar Mountains that pass through it.
Food
The United Arab Emirates' culinary culture is heavily inspired by Islam and adheres to the Quran's teachings. Arab families are used to using their right hands for eating and typically sit on the floor. The first option for UAE food is delectable Arabic food, which includes distinctive Arabic baked naan, entire roasted lamb, rice wrapped in leaves, and specific seasonings.
Economic situation
Oil production and the petrochemical sector are the key drivers of the UAE's economy, and it is a member of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). In addition, the UAE is actively pursuing the development of a knowledge economy, with information technology at its center, and is paying close attention to the study and advancement of renewable energy. In June 2009 the International Renewable Energy Agency decided to establish its headquarters in the city, Abu Dhabi. In addition, the United Arab Emirates is a member of the Greater Arab Free Trade Area, the Gulf Cooperation Council, and the Arab League.
Education
In addition to implementing a free education system, the UAE places a high value on the advancement of education and the development of homegrown scientific and technological skills. UAE nationals are eligible to study at foreign universities at government expense in addition to attending public universities and colleges in the country and a number of private universities for free. Out of all students in their last year of secondary school, 80% of male students and 95% of female students applied to study overseas or to enroll in UAE higher education institutions.


 Visa-free:142 countries
Visa-free:142 countries
 Diplomatic relations with China
Diplomatic relations with China
 Language:Arabic
Language:Arabic
 Capital:Abu Dhabi
Capital:Abu Dhabi

 10 years of renewable residence, long time.
10 years of renewable residence, long time.